Week 1 Day 3
New Terms
- Image
- Video
- Audio
- Inline Frame
Image
Definiton: An element that embeds an image into the document.
Description: The "src" attribute is a must—it tells the browser where to find your image. The "alt" attribute is essential for accessibility. Screen readers use it to describe images to visually impaired users, and if the image doesn’t load (because of a bad link or slow internet), the alt text shows up instead.

Video
Definition: An element that embeds a media player which supports video playback into the document.
Description: The "src" attribute specifies the video file's location, while the controls attribute adds playback controls like play, pause, and volume.
Attributes
- Autoplay: Starts the video automatically as soon as it's ready.
- Muted: Ensures the video plays without sound (useful for autoplay).
- Loop: Makes the video start over when it finishes.
- Poster: Displays an image as a preview before the video plays.
- Width and Height: Let you set the video size.
You can also use multiple source tags inside the video element to support different video formats for better compatibility across browsers.

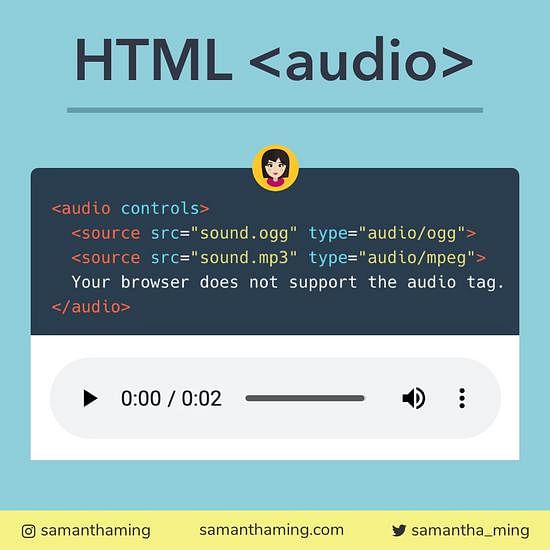
Audio
Definition: An element used to embed sound content into the document.
Description: The "audio" element in HTML allows you to embed sound files like MP3, Ogg, and WAV directly into a web page. Key attributes include "src" for the audio file path, "controls" for built-in playback controls, and "autoplay" to start the audio automatically. You can also use "loop" to make the audio repeat and "preload" to load it before playback. For accessibility, the "track" element lets you add captions or subtitles.
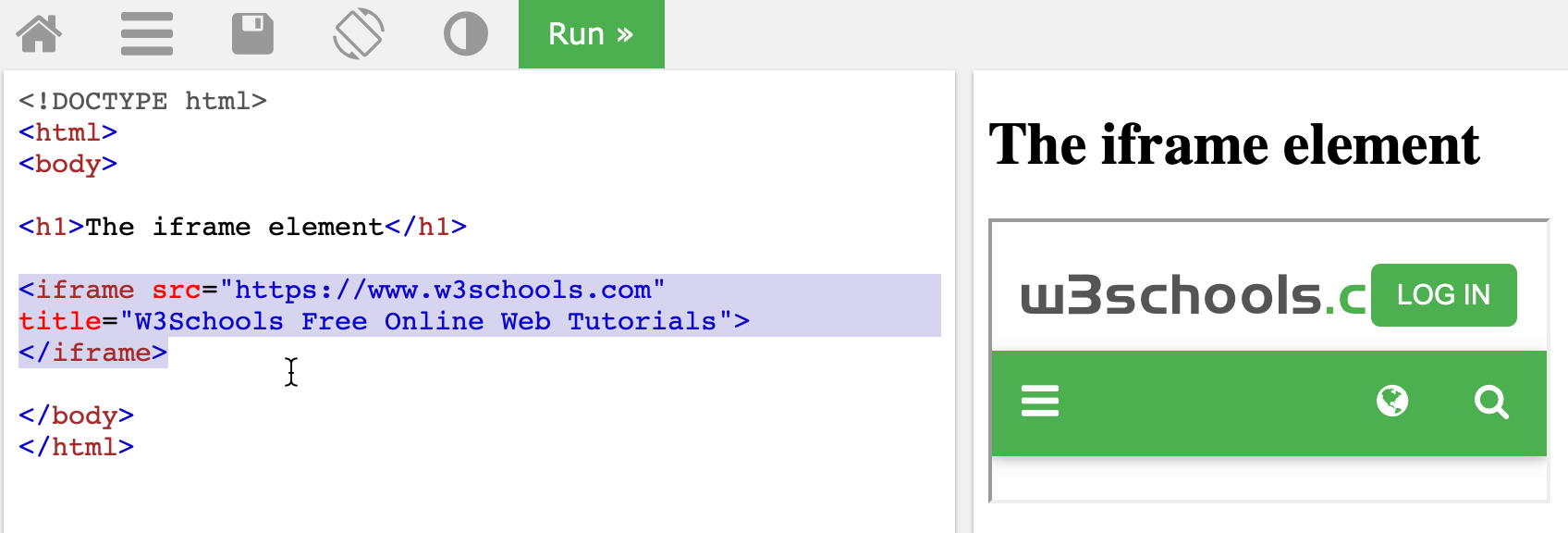
Inline Frame
Definiton: An element that embeds another HTML page into the current document.
Description: The "iframe" element in HTML lets you embed another webpage within your own, making it easy to show things like videos, maps, or even entire websites. The key attribute here is "src", which tells the browser where to pull the content from. You can set the size of the iframe using "width" and "height", and if you want to target it with links or scripts, you can give it a "name". For added security, the "sandbox" attribute puts some restrictions on the iframe, while "allowfullscreen" lets it go full-screen for things like videos. Lastly, the "loading" attribute controls when the iframe content loads, with options like "lazy" loading to improve performance.